
Blog
Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor – Arduino Simple Tutorial
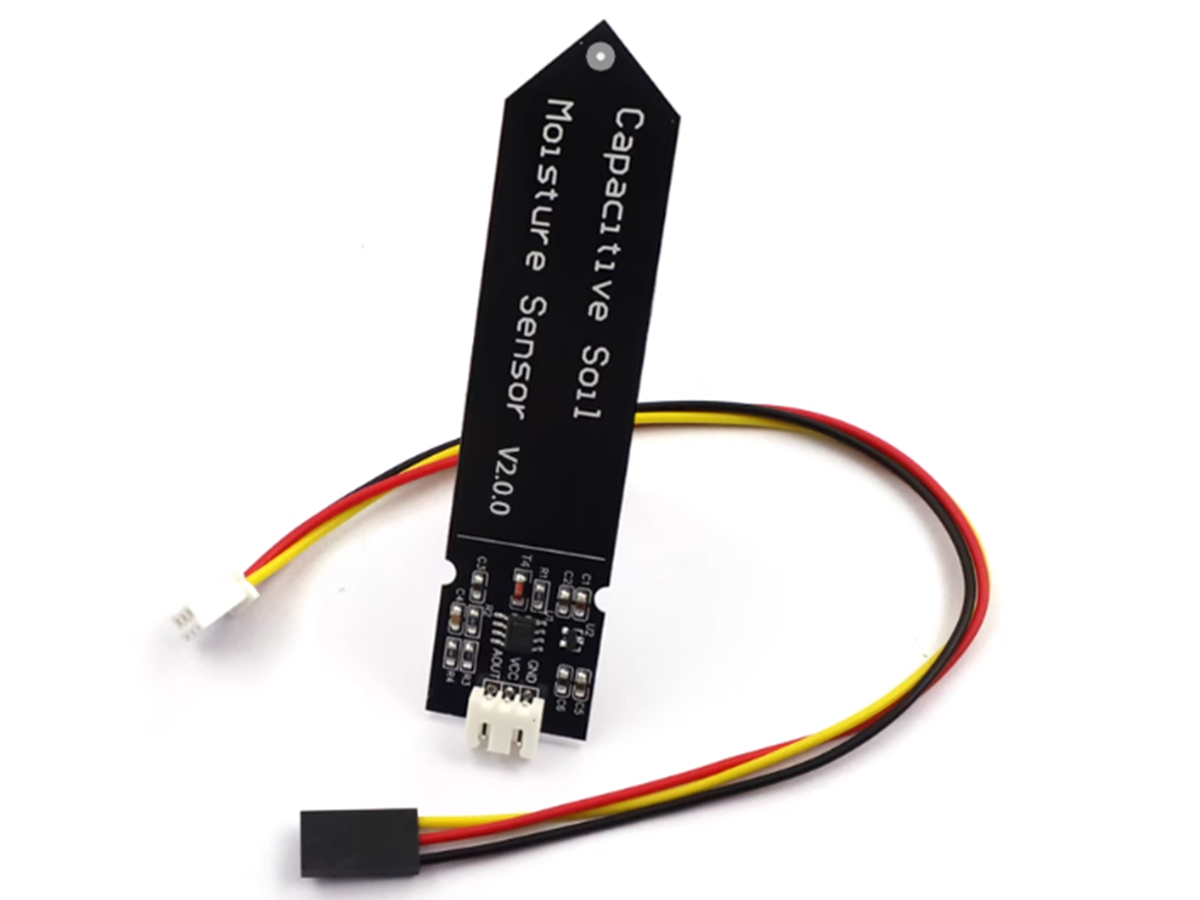

What is Soil Moisture Sensor?
Soil moisture sensor is an electronic device used to detect soil moisture. It determines the level of soil moisture by measuring the dielectric constant or resistance of the soil, and converts these signals into electrical signals for output, which can then be used by microcontrollers or microprocessors. This type of sensor is widely applied in fields such as agriculture, crop cultivation, environmental monitoring, and scientific research, enabling precise and efficient crop cultivation.
Types of Soil Moisture Sensors
Soil moisture sensors are mainly divided into two major types: Resistive sensors and Capacitive sensors.
Principle of Soil Moisture Sensor
| Comparison Dimension | Resistive Sensor | Capacitive Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Measures resistance/conductance between two exposed electrodes. More moisture increases ionic conductivity, lowering resistance. | Measures capacitance change using soil as dielectric. More moisture increases dielectric constant, raising capacitance. |
| Electrode Structure | Directly exposed metal probes contacting soil and moisture. | Coated/covered electrodes, physically isolated from soil, sensing via electromagnetic fields. |
| Accuracy & Reliability | Lower. Highly affected by salinity, fertilizers, temperature; poor long-term stability. | Higher. Less affected by salinity; good long-term stability; mainstream technology. |
| Corrosion Issue | Severe. Electrochemical corrosion from continuous current causes rapid failure. | Minimal. Protected electrodes prevent electrochemical reactions; long lifespan. |
| Power Consumption | Higher. Requires continuous power, may cause soil electrolysis. | Very low. Powers only during measurement; ideal for battery-powered projects. |
| Cost | Very low. Simple structure, lowest manufacturing cost. | Moderate. More expensive but better cost-effectiveness; preferred for hobby/commercial use. |
| Calibration | Difficult. Requires individual calibration for different soil types, especially salinity. | Easier. Still needs calibration but less sensitive to soil chemistry. |
| Main Advantages | Low cost, simple circuitry, easy to make, suitable for beginners. | High accuracy/reliability, corrosion-resistant, low power, long lifespan. |
| Main Disadvantages | Prone to corrosion, low accuracy, affected by environment, requires frequent replacement. | Higher cost than resistive, still requires calibration in highly saline/alkaline soils. |
| Typical Applications | Disposable/short-term uses: educational experiments, simple toys with low accuracy/lifespan demands. | Smart agriculture irrigation, automated gardening, scientific experiments, environmental monitoring. |
| Common Models | Unbranded low-cost modules (usually with two exposed probes). | Arduino community sensors: Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor, Seeed Studio Grove – Capacitive, DFRobot. |
Common Models of Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensors
In daily use and learning, the following capacitive soil moisture sensor is very common. It has three main versions: v1.0, v1.2, and v2.0, among which versions 1.2 and 2.0 are both modified and upgraded from version 1.0. It works on the principle of capacitive sensing, with high corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it an ideal choice for understanding and learning about soil moisture sensors.

Electrical Performance of Soil Moisture Sensors
| Product Name | Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3~5.5 VDC |
| Output Voltage | 0~3.0 VDC |
| Interface | PH2.0-3P |
| Dimensions | 98(L) × 23(W) | mm |
Introduction to the Pinout of Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensors
This capacitive soil moisture sensor adopts a typical three-wire interface and outputs an easy-to-understand digital signal, which facilitates subsequent processing and use. When in use, it is important to note that the sensor should not be inserted beyond the warning line; otherwise, the circuit may be easily corroded.

Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensors Size

Simple Demonstration of Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor Output Signal with Arduino
Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensors Arduino Project:
Before using this capacitive soil moisture sensor, we need to understand the signal format output by this module. In the following examples, the software used is Arduino IDE, and the hardware is Arduino Uno, capacitive soil moisture sensor v2.0.
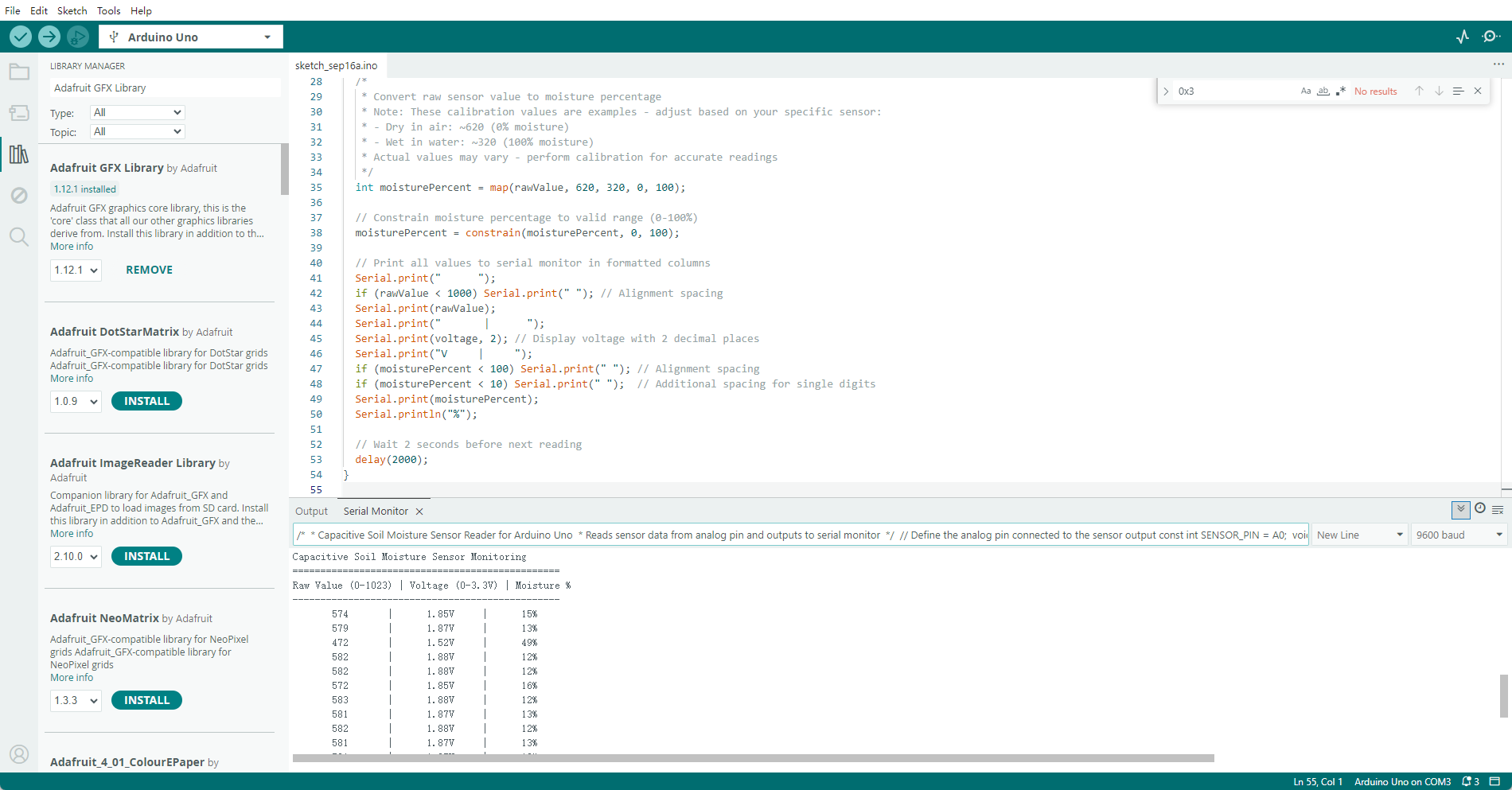
/*
* Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor Reader for Arduino Uno
* Reads sensor data from analog pin and outputs to serial monitor
*/
// Define the analog pin connected to the sensor output
const int SENSOR_PIN = A0;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud rate
Serial.begin(9600);
// Print header information to serial monitor
Serial.println("================================================");
Serial.println("Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor Monitoring");
Serial.println("================================================");
Serial.println("Raw Value (0-1023) | Voltage (0-3.3V) | Moisture %");
Serial.println("------------------------------------------------");
}
void loop() {
// Read raw analog value from sensor (0-1023)
int rawValue = analogRead(SENSOR_PIN);
// Convert raw value to voltage (0-3.3V)
float voltage = rawValue * (3.3 / 1023.0);
/*
* Convert raw sensor value to moisture percentage
* Note: These calibration values are examples - adjust based on your specific sensor:
* - Dry in air: ~620 (0% moisture)
* - Wet in water: ~320 (100% moisture)
* Actual values may vary - perform calibration for accurate readings
*/
int moisturePercent = map(rawValue, 620, 320, 0, 100);
// Constrain moisture percentage to valid range (0-100%)
moisturePercent = constrain(moisturePercent, 0, 100);
// Print all values to serial monitor in formatted columns
Serial.print(" ");
if (rawValue < 1000) Serial.print(" "); // Alignment spacing
Serial.print(rawValue);
Serial.print(" | ");
Serial.print(voltage, 2); // Display voltage with 2 decimal places
Serial.print("V | ");
if (moisturePercent < 100) Serial.print(" "); // Alignment spacing
if (moisturePercent < 10) Serial.print(" "); // Additional spacing for single digits
Serial.print(moisturePercent);
Serial.println("%");
// Wait 2 seconds before next reading
delay(2000);
}
As can be seen, this module changes the output voltage and feeds back a numerical value. During use, this value can be converted into a specific percentage for application and processing.
FAQ
How Long Can a Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor Work?
A capacitive soil moisture sensor can generally be used for 2 to 5 years, depending on your usage method and the environment. A favorable environment can extend its service life.
