
Blog
In depth guide to the ldr relay switch
What Is a LDR Relay Switch?
A Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) relay switch is an intelligent electronic control system that automatically turns electrical devices ON or OFF based on ambient light intensity. This type of circuit is widely used in automatic street lights, smart home lighting, security systems, and energy-saving applications.
What Is a Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)?
A Light Dependent Resistor, also known as a photoresistor, is a passive electronic component whose resistance varies with light intensity.
- High light intensity → Low resistance
- Low light intensity (darkness) → High resistance
This property makes LDRs ideal for light-sensing applications.
What Is a Relay Switch?
A relay is an electrically operated switch that allows a low-power control signal (from an Arduino or transistor) to safely switch high-voltage or high-current loads, such as:
- AC lamps
- Motors
- Fans
- Heaters
Using a relay provides electrical isolation between control and load circuits.
Working Principle of an LDR Relay Switch
The LDR relay switch operates on the principle of light-controlled resistance change:
- The LDR senses ambient light.
- Its resistance changes accordingly.
- This change is converted into a voltage signal.
- The signal triggers a relay module.
- The relay switches an external device ON or OFF.
Example:
- Daylight → Relay OFF → Light OFF
- Nighttime → Relay ON → Light ON
Key Components Used in an LDR Relay Circuit
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| LDR | Senses light intensity |
| Arduino Uno | Processes sensor data |
| Relay Module (5V) | Controls high-power load |
| Resistor (10kΩ typical) | Voltage divider |
| Power Supply | 5V DC |
| Load (Lamp, Fan, etc.) | Controlled device |
LDR Relay Switch Circuit Diagram
Basic LDR Relay Switch Circuit Diagram

This diagram shows the basic working concept of an LDR-controlled relay switch.
- The LDR and resistor form a voltage divider
- The output voltage varies with light intensity
- This signal is used to:
- Drive a transistor OR
- The relay safely switches high-voltage AC or DC loads
How the Circuit Works
- Light falls on the LDR
- Resistance changes based on brightness
- Relay activates or deactivates
- External load switches ON or OFF automatically
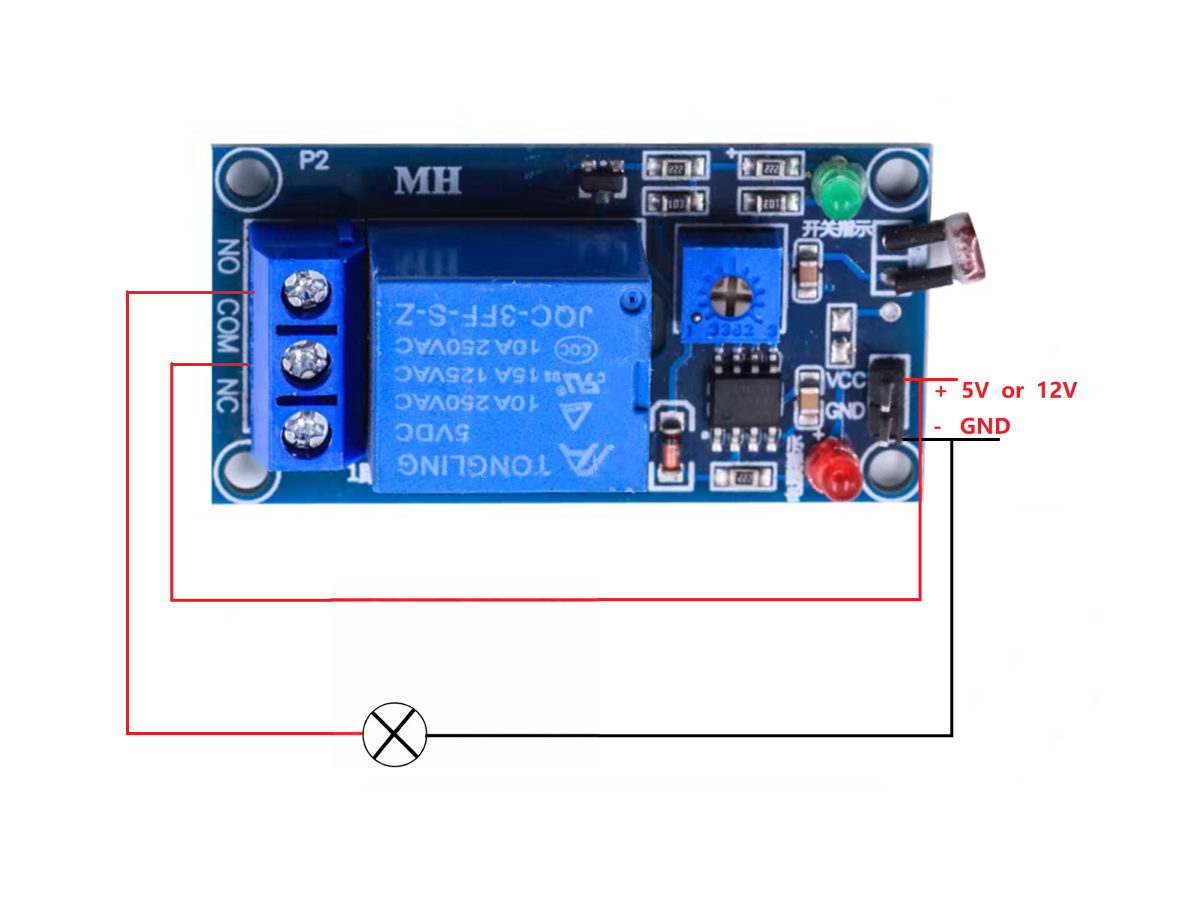
Wiring Method
Method 1: No additional power supply for the load
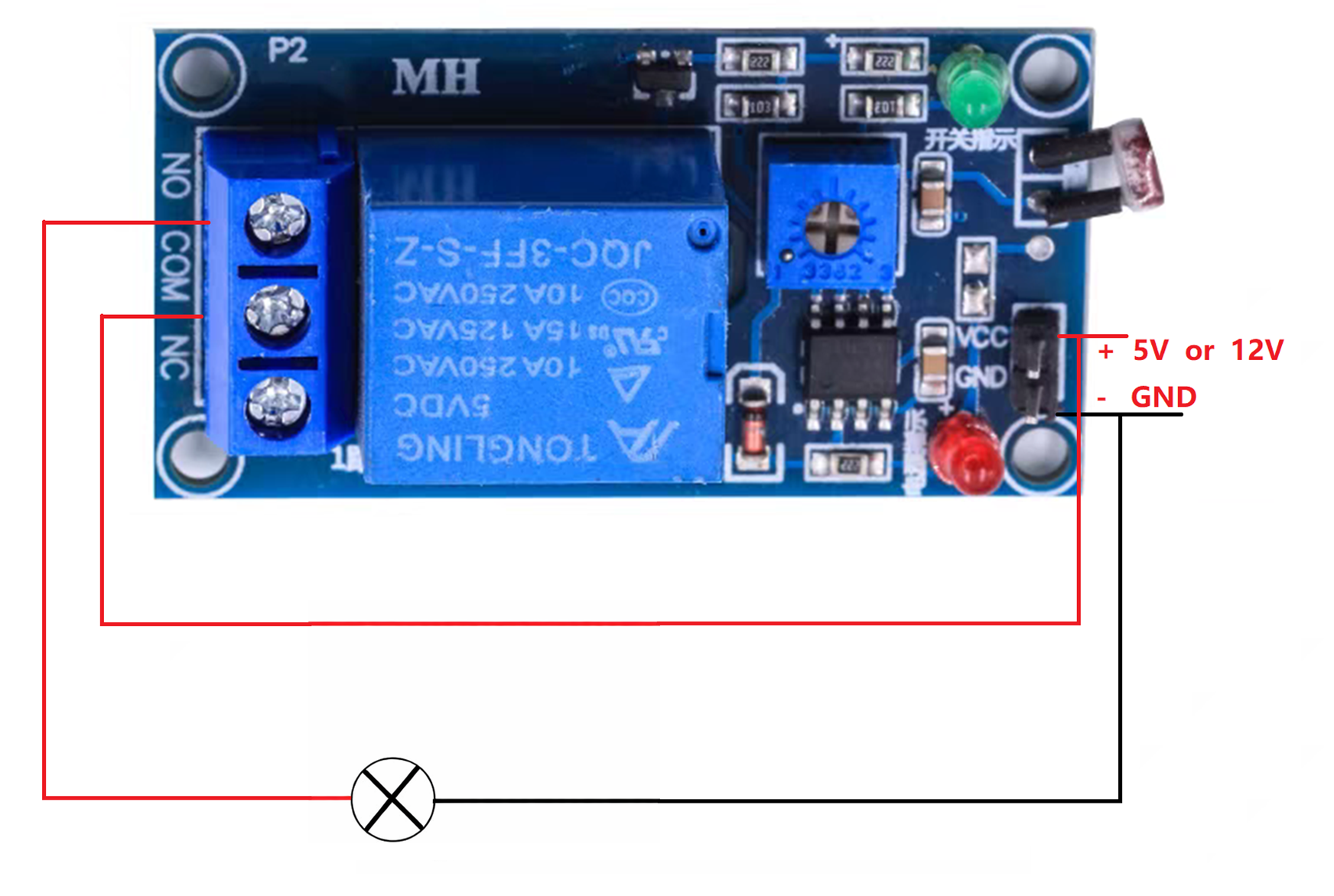
Method 2: Provide additional power supply for the load

Applications of LDR Relay Switches
- Automatic street lighting
- Smart home automation
- Garden and outdoor lights
- Energy-saving systems
- Security lighting
- Solar-powered systems
Advantages of LDR Relay Switch Circuits
- Low cost
- Easy to implement
- Energy efficient
- Reliable and durable
- Minimal maintenance
Limitations and Considerations
- LDRs are temperature-sensitive
- Response time is slower than photodiodes
- Not ideal for precision light measurement
- AC loads require proper isolation and safety precautions
FAQ
1. What is an LDR relay switch used for?
An LDR relay switch is used for automatic control of electrical devices based on ambient light, such as turning lights ON at night and OFF during the day.
2. Can I connect an LDR directly to a relay?
No. An LDR cannot directly drive a relay. You need a transistor, comparator, or microcontroller (Arduino Uno) to process the signal.
3. How do I adjust light sensitivity?
By changing the threshold value in the code or adjusting the resistor value in the voltage divider.
4.What happens to the LED when the LDR is covered?
When much light fall on the LDR, then the LED brightness will increase and when the LDR covered with something or taken into a dark place, then it will automatically adjust the brightness of the LED. That means it will dim the LED.
5.What is the difference between a resistor and an LDR?
An LDR is also called a photo-resistor or photocell or photoconductive cell. A photodiode is mainly designed to operate in reverse bias condition. LDRs are mostly used in forward bias condition. A photodiode acts as a unidirectional resistor.
