
Blog
MT3608 Boost Board: A Comprehensive Guide from Principles to Applications
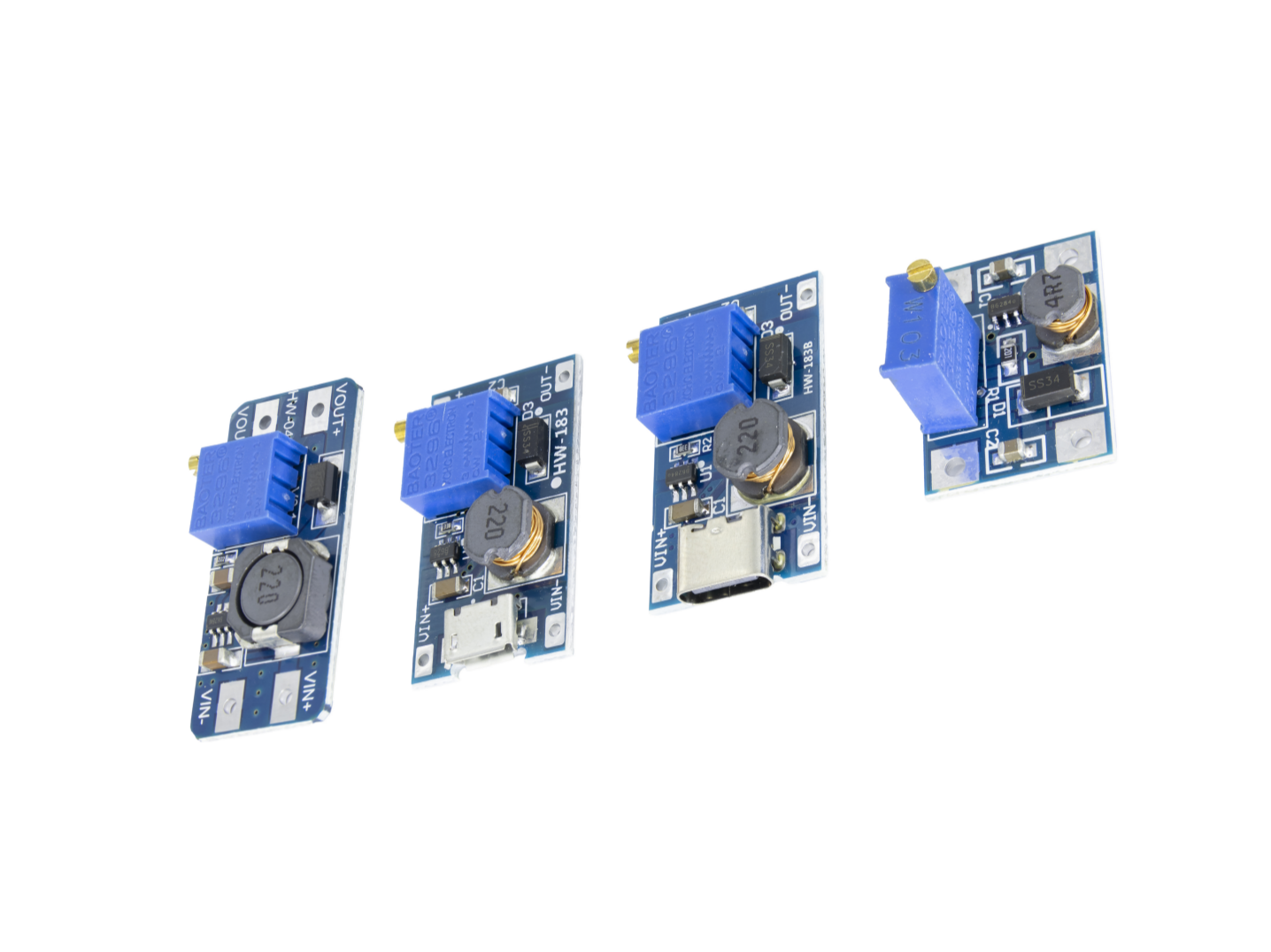
Today we’d like to share insights on boost converters. These versatile components come in various types and find applications across numerous fields. This article will take you on an in-depth journey from the principles behind boost converters to their practical applications!
In electronics projects, portable device repairs, or DIY endeavors, we often encounter a tricky problem: the device requires a higher voltage than the power supply provides. For instance, powering a microcontroller or LED module that needs 5V with a 3.7V lithium battery demands a core component capable of “boosting voltage”—the boost board. Among numerous boost converter solutions, the MT3608 has become a popular choice among electronics enthusiasts and engineers due to its compact size, high efficiency, and low cost. Today, we’ll thoroughly dissect this “voltage magician,” covering everything from its principles to practical applications, empowering you to master its use with ease.
What is MT3608? — More than just a “small circuit board”
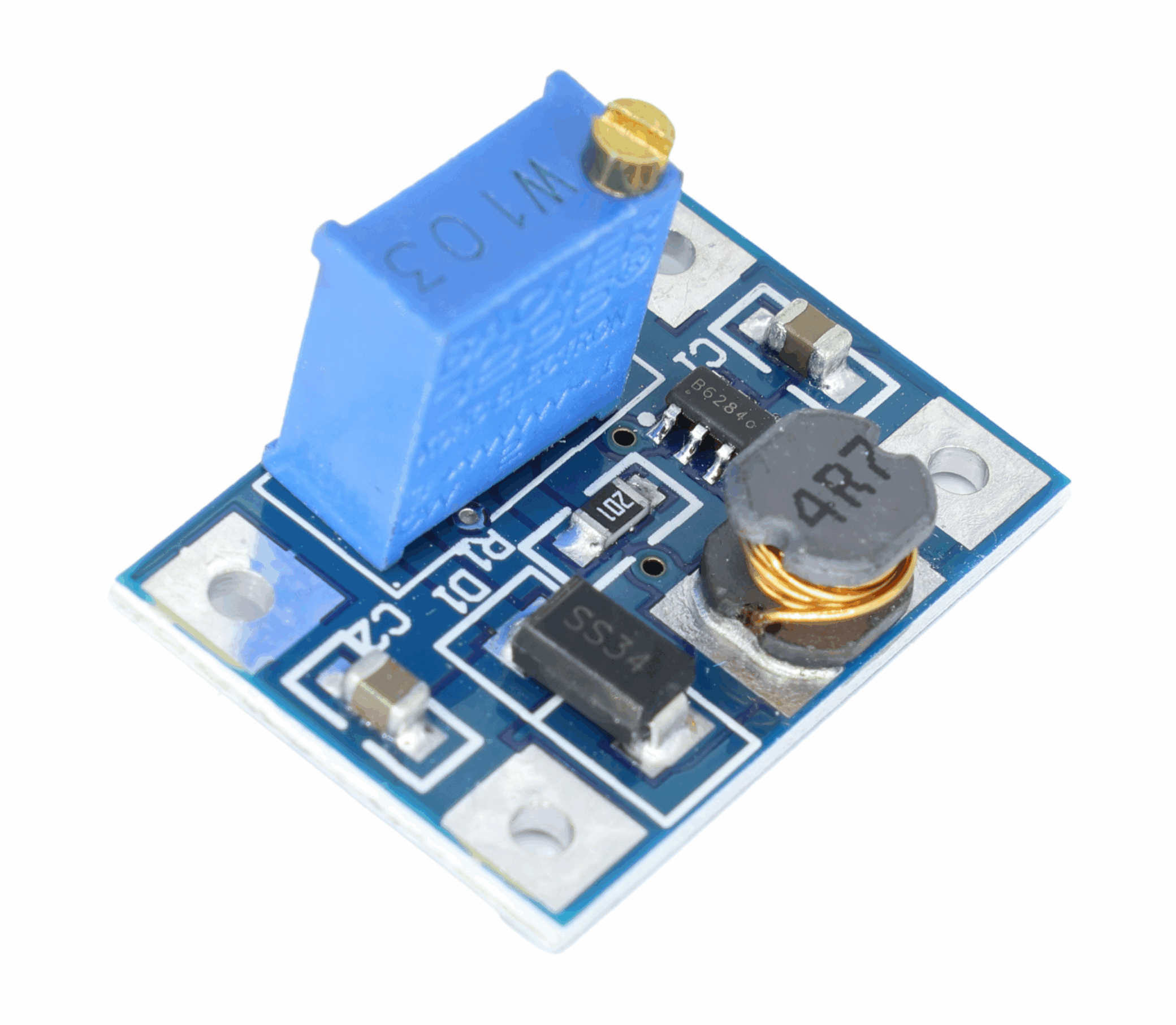
First, it’s important to clarify: The MT3608 is fundamentally a synchronous rectification boost DC-DC converter chip. What we commonly refer to as the “MT3608 boost board” is actually a “modular product” that integrates the MT3608 chip with peripheral components such as inductors, capacitors, and resistors. This modular design significantly lowers the user’s entry barrier, eliminating the need for complex soldering of peripheral circuits. Users simply connect the input power source and load to achieve voltage step-up functionality.
Core Advantages of MT3608
- Ultra-compact size: The common MT3608 module measures only about 20mm × 15mm (roughly the size of a fingernail), enabling seamless integration into small devices such as Bluetooth earbuds and smart bracelet charging modules.
- Wide Input Voltage Range: The input voltage typically spans 2V to 24V, covering common low-voltage power sources like 1.5V alkaline batteries, 3.7V lithium batteries, and 12V lead-acid batteries.
- High Output Voltage and Current: The output voltage can be adjusted via a potentiometer from 5V to 28V, with a maximum output current of 2A (actual continuous output is recommended to be kept below 1.5A to prevent overheating).
- High Efficiency: Synchronous rectification technology achieves conversion efficiency exceeding 92%, significantly exceedingtraditional linear regulators (e.g., 7805, often below 50% efficiency). This effectively reduces power waste and module heat generation.
MT3608 DATASHEET
Here we provide you with the MT3608 datasheet for your reference.
MT3608 How Does It “Boost Voltage”? — Core Principle Breakdown
Many people wonder: How can such a tiny chip “transform” low voltage into high voltage? In fact, the core principle of the MT3608 is high-frequency switching based on “inductor energy storage – capacitor energy release,” which can be broken down into three steps:
- Inductor Energy Storage: “Charging” Phase
When the internal switch (MOSFET) of the MT3608 closes, the input power source (e.g., a 3.7V lithium battery) supplies electricity to the module’s inductor. At this point, the inductor acts like a “battery” to store electrical energy. The current gradually increases while a magnetic field forms around the inductor. The core function of this stage is “energy storage,” akin to coiling a spring.
- Capacitor Energy Release: “Discharge” Phase
When the switch turns off, the magnetic energy stored in the inductor converts to electrical energy. Due to the inductor’s inherent resistance to sudden current changes, it generates an induced voltage higher than the input voltage—this is the key to “boosting.” At this point, the diode on the module conducts, transferring the high-voltage energy generated by the inductor to the output capacitor while simultaneously powering the load (e.g., a 5V device).
- High-Frequency Switching: Stable Output
MT3608 controls the “close – open” cycle of the switching tube at an extremely high frequency (about 1.2MHz), switching more than 1 million times per second. At the same time, the feedback circuit inside the module monitors the output voltage in real time. Once the voltage is lower than the set value, it will adjust the on – time of the switching tube to ensure that the output voltage stabilizes at the target value (such as 5V, 12V).
Simply put, MT3608 is like a “high – speed porter”: through high – frequency switching, it “packages” the low – voltage electric energy of the input power supply and stores it in the inductor, and then “transports” it to the output end in the form of high voltage, thus realizing voltage boosting.
How to Use MT3608? — Wiring and Debugging Guide
The MT3608 module is extremely easy to use, allowing even electronics beginners to get started quickly. Let’s take “powering a 5V microcontroller with a 3.7V lithium battery” as an example to explain the specific steps:
1.First, let’s get to know the pins of the module.A common MT3608 module has 4 pins (some simplified versions have 3 pins, omitting the “enable pin”). From left to right, they are:
- OUT+: Output voltage positive terminal (connects to load positive, such as the microcontroller’s VCC pin);
- IN+: Input voltage positive terminal (connect to power supply positive, e.g., lithium battery positive terminal);
- OUT-: Output voltage negative terminal (connects to load negative, e.g., microcontroller GND pin);
- IN-: Input voltage negative terminal (connects to power source negative, e.g., lithium battery negative);
- (Optional) EN: Enable pin (active high; connects to high to activate module, low to sleep mode; can control module power cycling).
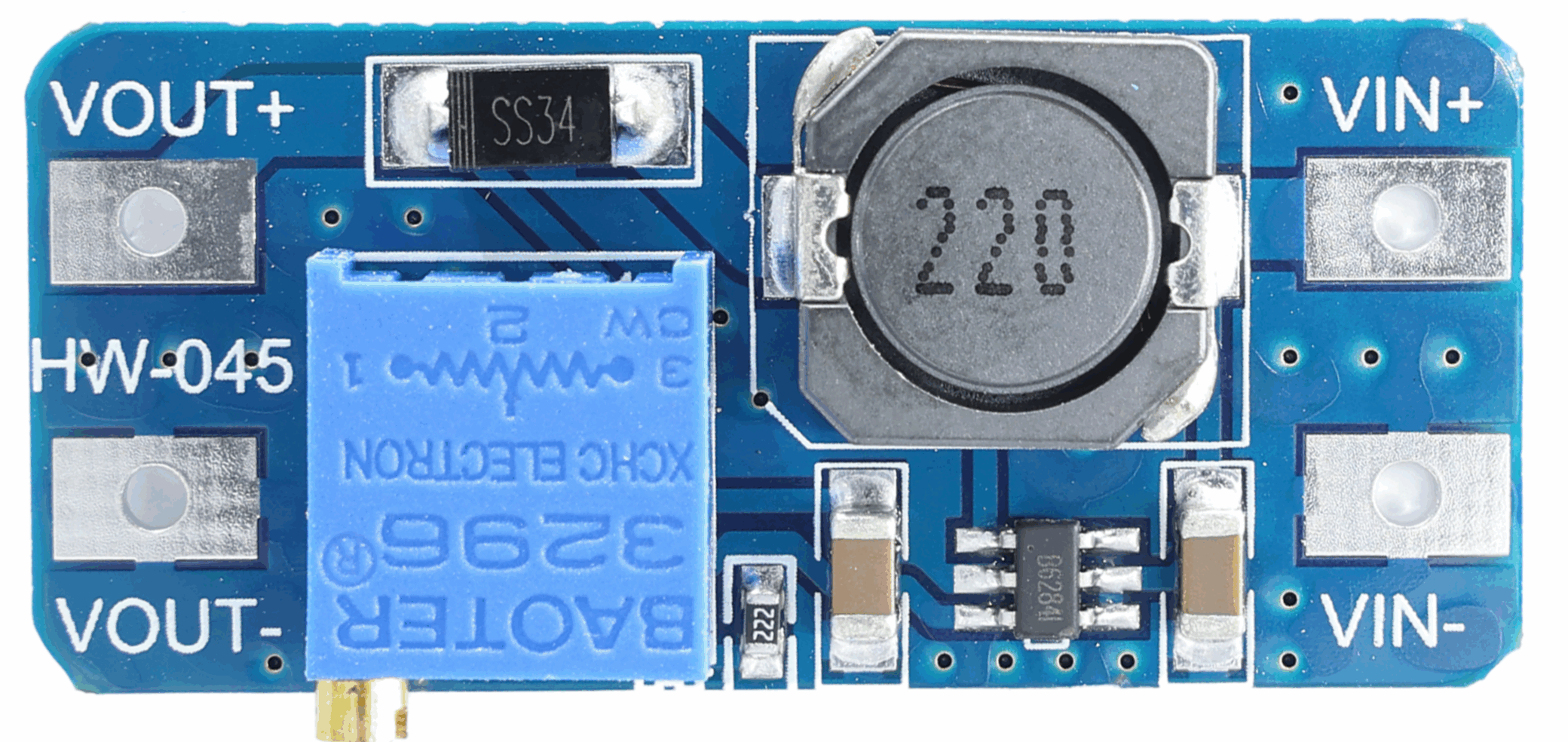
2.Wiring Steps (Crucial!)
Wiring Principle: Connect the input first, then adjust the voltage, and finally connect the load (to prevent the load from being damaged due to unstable voltage):
Connect the input power supply: Connect the positive pole of the 3.7V lithium battery to IN+, and the negative pole to IN- (Note: The positive and negative poles must not be reversed, otherwise the module may be burned out);
Adjust the output voltage: Set the multimeter to the “DC voltage range”, connect the red test lead to OUT+ and the black test lead to OUT-, then slowly turn the potentiometer (the blue or orange knob marked “ADJ”) on the module with a small screwdriver, and observe the multimeter reading until it shows 5V;
Connect the load: After confirming that the output voltage is stable at 5V, connect the VCC of the single-chip microcomputer to OUT+ and GND to OUT-, and the wiring is completed.
3. Precautions
- 1、The input voltage must not exceed the module’s maximum input voltage (typically 24V), otherwise it will burn out the MT3608 chip;
- 2、 Output current must not exceed 1.5A continuously (the module will activate thermal protection or may be damaged). For high-current loads (e.g., motors, high-power LEDs), install additional heat sinks.
- 3、 When placing the module near high-power components, ensure proper shielding (to prevent electromagnetic interference affecting output stability).
Typical Application Scenarios for MT3608
With its compact and efficient design, the MT3608 finds extensive applications across various fields including consumer electronics, DIY projects, and industrial control:
- Powering Portable Devices
- ·Supplying 5V power to USB fans and LED desk lamps using 3.7V lithium batteries;
- ·Designing boost charging circuits for backup batteries in Bluetooth speakers and action cameras.
- Electronics DIY Projects
- Boost 3.7V lithium batteries to 5V or 3.3V (requires a voltage regulator module) in Arduino, ESP32, and other microcontroller projects;
- Build a simple emergency power bank by boosting 1.5V alkaline batteries (2 in series for 3V) to 5V for temporary phone charging.
- Device Repair and Modification
- Repair power modules in older devices (e.g., damaged 12V power supplies in routers or set-top boxes; use MT3608 to boost 5V adapter to 12V);
- Modify automotive electronics (e.g., boost car’s 12V power to 24V for dashcams or car refrigerators).
Module Selection and Pitfall Avoidance: How to Choose a Reliable MT3608 Module?
The quality of MT3608 modules on the market varies greatly. Some inferior modules have problems such as low efficiency, severe heat generation, and unstable output. When purchasing, we need to pay attention to the following 3 points:
- Check the authenticity of the chip:High-quality modules will clearly mark the “MT3608” chip model (which can be observed with a magnifying glass). Inferior modules may use refurbished chips or unknown alternative chips, and their efficiency will be much lower.
- Check peripheral components:For the inductor, choose a shielded inductor (which looks like a black cube without exposed coils). For the capacitor, use a surface-mounted electrolytic capacitor or solid capacitor (to avoid leakage of liquid capacitors).
- Check output stability:It can be tested with a multimeter — when fully loaded (such as with a 1A load), the output voltage fluctuation should be less than 0.1V. If the fluctuation is too large, it indicates that the voltage regulation performance of the module is poor.
(If you need it, we can provide you with high-quality MT3608 modules.)
Regarding model selection, you can purchase different versions of MT3608 according to your different needs.
2A booster board (ordinary version):

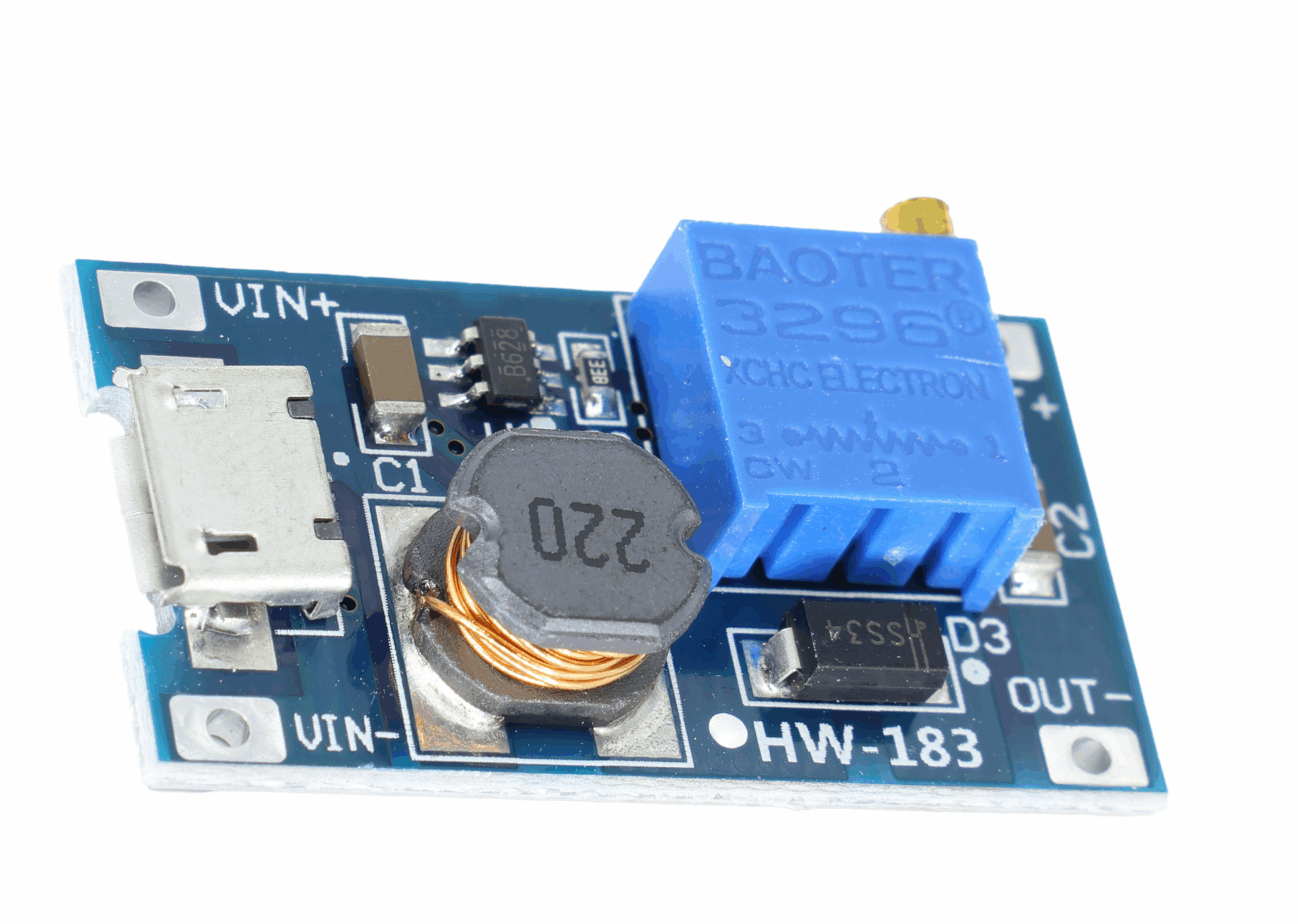
2A booster board with TYPE-C port: It can use Type-C USB input. You can connect the booster board with a USB charger or a power bank via a mobile phone data cable, and easily get common voltages like 9V, 12V, 15V, 18V, 24V.
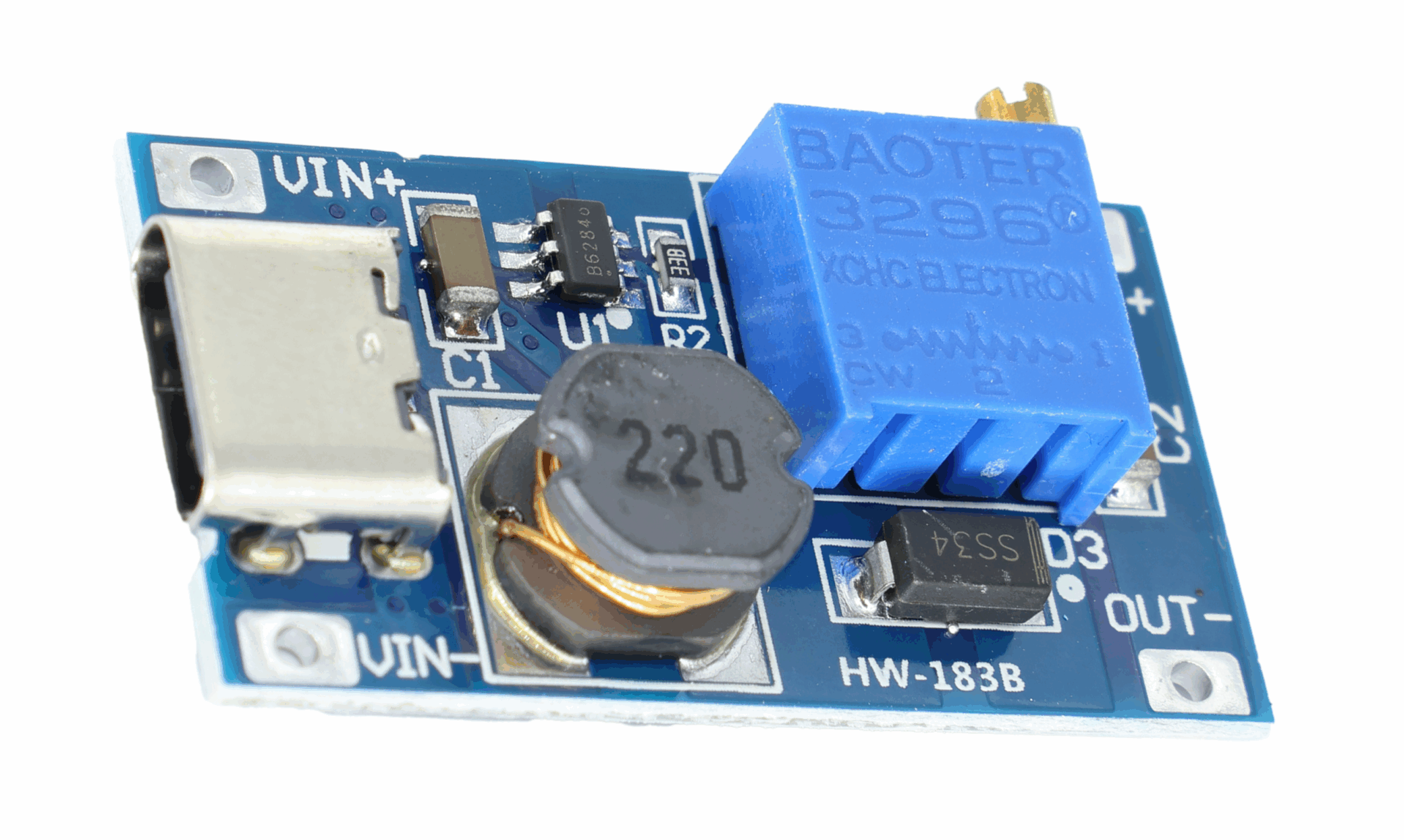
2A booster board with MICRO port: It can use Micro USB input. You can connect the booster board with a USB charger or a power bank via a mobile phone data cable, and easily get common voltages like 9V, 12V, 15V, 18V, 24V.
SX1308 DC-DC adjustable booster board 2A: It has an SX1308 chip inside. It features small package, high efficiency, and adjustable output voltage. It integrates a metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor with extremely low RDS on-resistance of 100mΩ, which can achieve large current output within 2A.
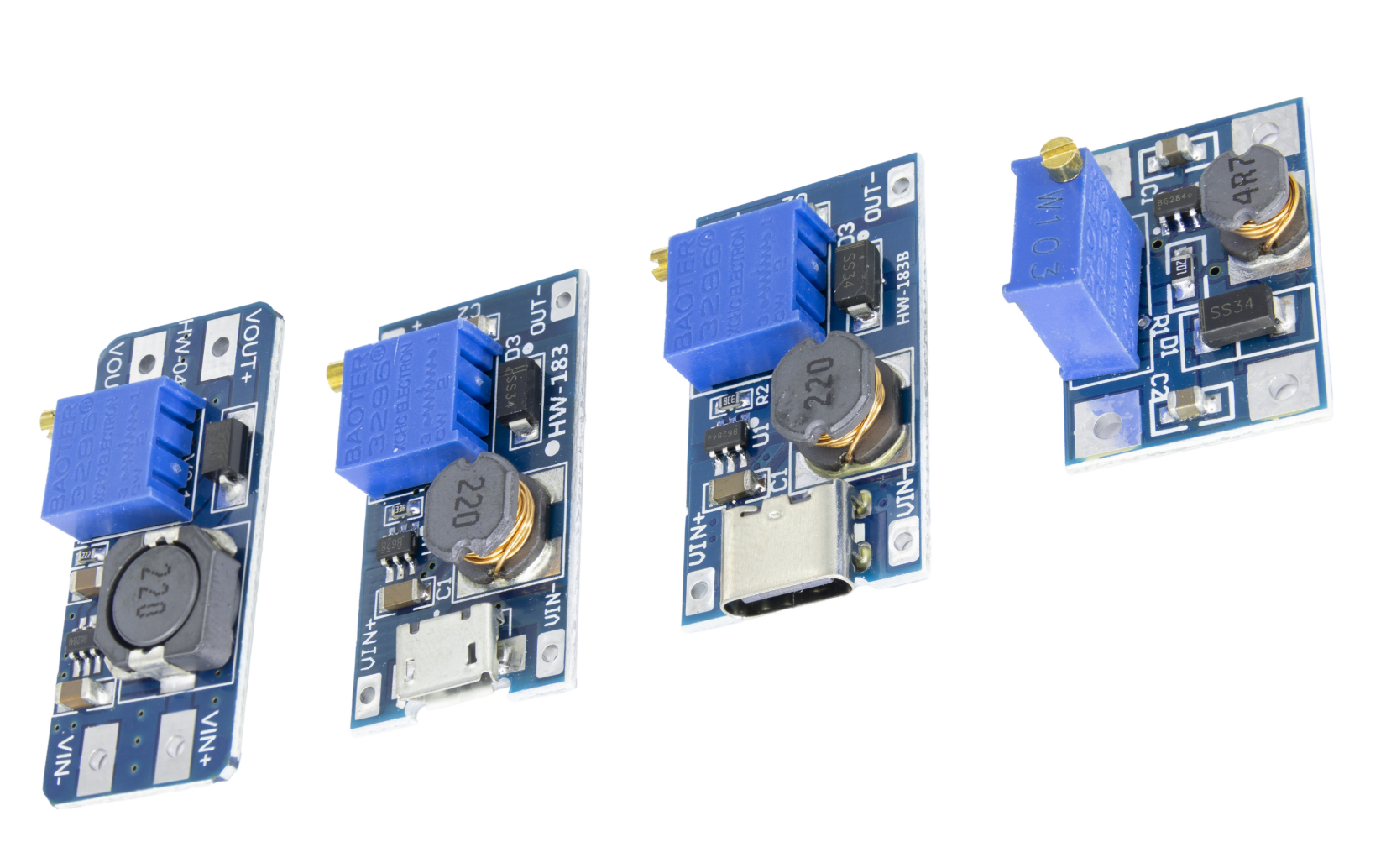
Product Collection

Summary: The Strengths and Limitations of the MT3608
MT3608 is undoubtedly a “best – value – for – money” level boosting component. Its advantages (small size, high efficiency, and easy to use) make it the first choice for low – voltage boosting scenarios. But it also has limitations: it can’t be used for AC voltage boosting (only supports DC – DC conversion). And when the output voltage is too high (such as 28V) or the load current is too large (such as 2A), heat dissipation and protection measures must be taken.
For electronic enthusiasts, MT3608 is not only a practical component, but also an excellent carrier to understand the “switching power supply principle”. Through it, we can more intuitively feel the practical application of abstract concepts such as “inductor energy storage” and “synchronous rectification”. If you are working on a low – voltage equipment power supply project, you might as well try MT3608. I believe it will bring you the convenient experience of “adjusting the voltage as you like”.
FAQS
What is the difference between MT3608 and XL6009?
Comparison Item | MT3608 | XL6009 |
Switch Frequency | Generally high (kHz level and above); Inductor: 4.7 – 22μh | 400kHz (lower, allows smaller filter components) |
Input Voltage Range | 2 – 24V (some modules support wider range) | 3 – 32V (min input ≥5V; 3V input reduces efficiency sharply) |
Output Current | Typical rated: 2A (varies by scenario) | Some modules: up to 4A (varies by design) |
Output Voltage | Adjustable (5V/9V/12V/28V, etc.) | Fixed (3.3V/5V/12V) or adjustable |
Size | Relatively small | Larger (e.g., 45×20×14 mm) |
No – load Current | Low (with 5V input) | 15mA (higher than MT3608 with 5V input) |
Conversion Efficiency | Better (outperforms XL6009 in proper conditions) | Lower (e.g., 87.8% at 300A output) |
Application Scenarios | Cost – sensitive, small – size devices (e.g., multimeter power supply) | High – current, wide input range devices (e.g., car electronics) |
Can MT3608 power a small motor?
MT3608, a DC-DC boost chip, can theoretically drive small motors, but practical use depends on:
1、Output Current: Its typical rated output is 2A, yet small motors need large current at startup.
2、Output Voltage: It can adjust voltage to 5V/9V/12V, but must match the motor’s rated voltage.
3、Motor Type:
- DC brushed motors: Easy to drive if voltage and current match.
- Stepper/brushless DC motors: Need extra driver chips/circuits as MT3608 only boosts voltage, not providing complex control signals for direction/speed/steps.
