
Blog
Plug and Play! E16 GPRS AT Command Module for Quick Device Data Transmission
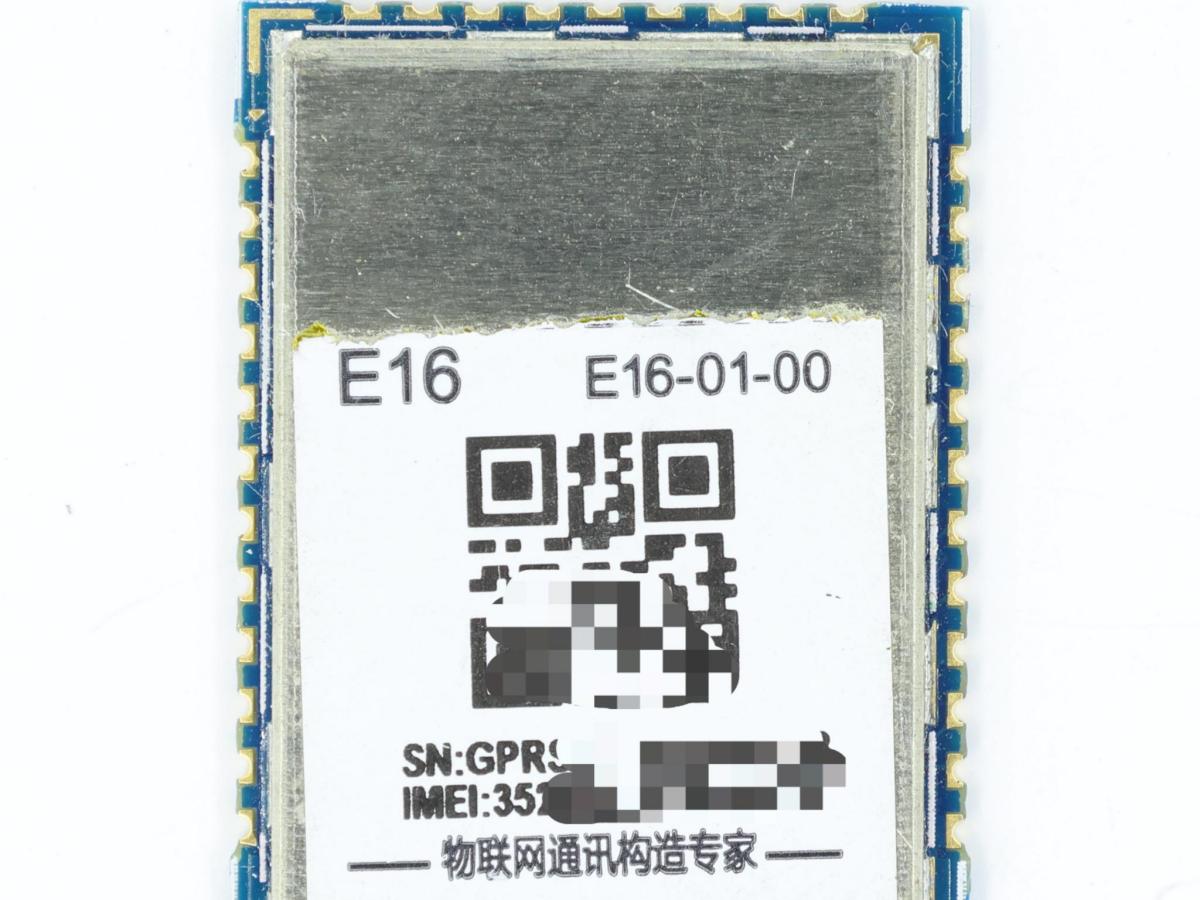
GPRS and GSM are wireless communication technologies widely used in the field of mobile communications, and the E16 GPRS AT Command Module is a powerful communication module developed based on these technologies. It supports a standard set of AT commands, allowing developers to easily configure and control it via a serial port, enabling wireless transmission and reception of data.
To gain a deep understanding of the E16 GPRS AT Command Module, we first need to clarify: What is GSM? And what is GPRS?
What is a GSM ?
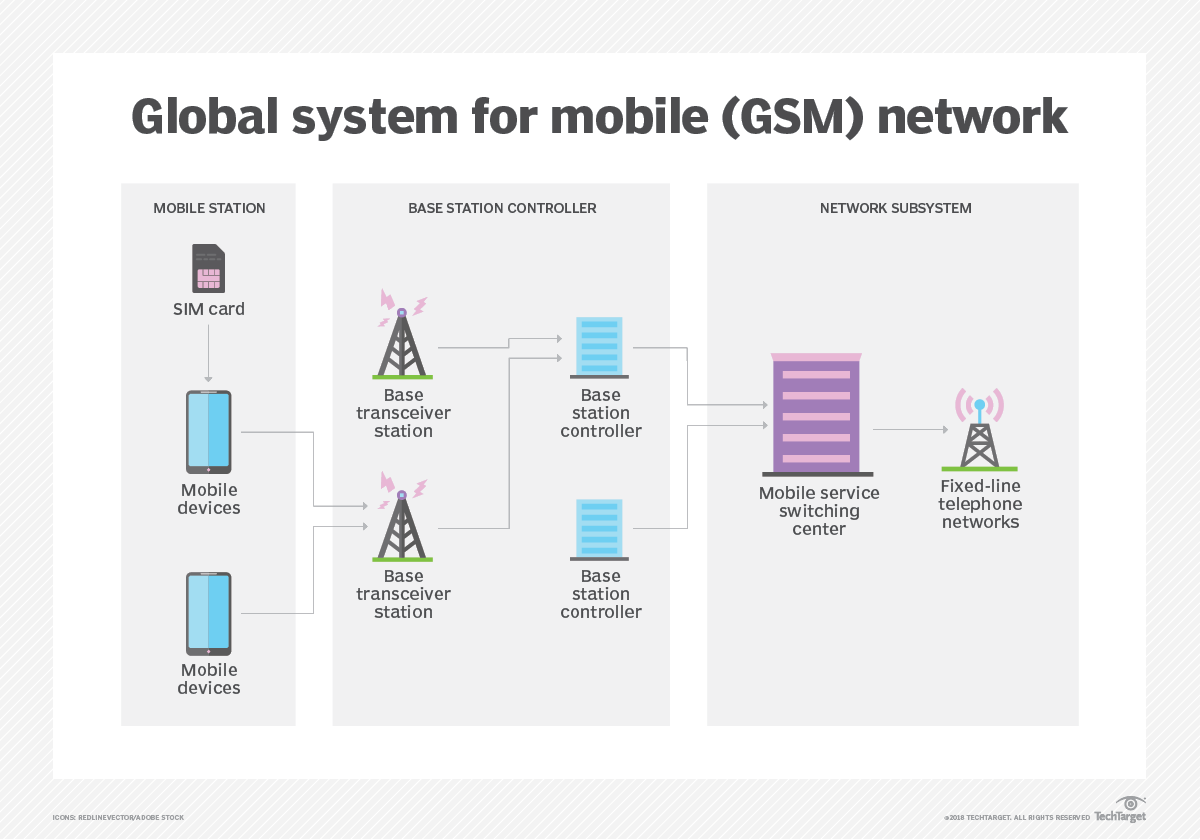
GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communications, the core standard for second-generation mobile communication technology (2G). It was officially commercialized in the early 1990s, adopting Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) technology and digital modulation. It operates on multiple frequency bands such as 850MHz, 900MHz, and 1800MHz, and now covers over 200 countries and regions worldwide.
This standard not only supports basic voice calls and SMS services but also enables data transmission (with a maximum rate of 9.6kbps). It uses a SIM card for user identity authentication and network access management, laying a standardized, global technical foundation for modern mobile communications.
What is a GPRS ?
GPRS stands for General Packet Radio Service, an intermediate technology that bridges GSM networks to third-generation mobile communications (3G). First proposed in 1997, GPRS adds a Packet-Switched (PS) domain to the existing GSM network architecture, enabling traffic-based billing and high-speed data transmission (with a theoretical peak rate of 171.2kbps).
This technology breaks the bandwidth limitations of traditional GSM circuit switching, supports IP and X.25 protocols, and allows mobile devices to stay connected to the internet continuously. It provided crucial technical support for the early development of the mobile internet.
What is a GSM module?
A GSM module (or GPRS module) is a type of chip or circuit that enables communication between mobile devices/computers and GSM/GPRS systems. A modem (short for modulator-demodulator) is its key component.
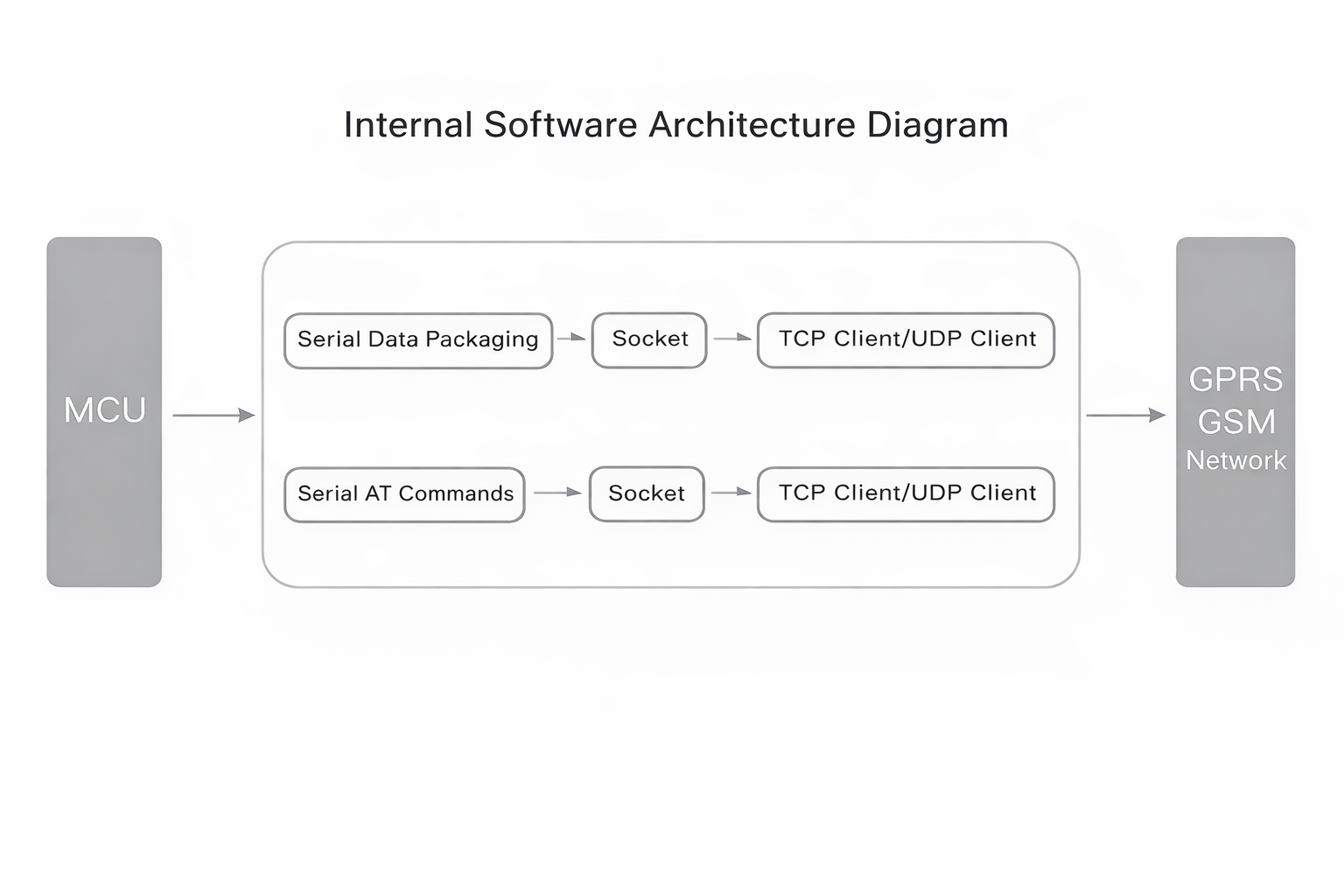
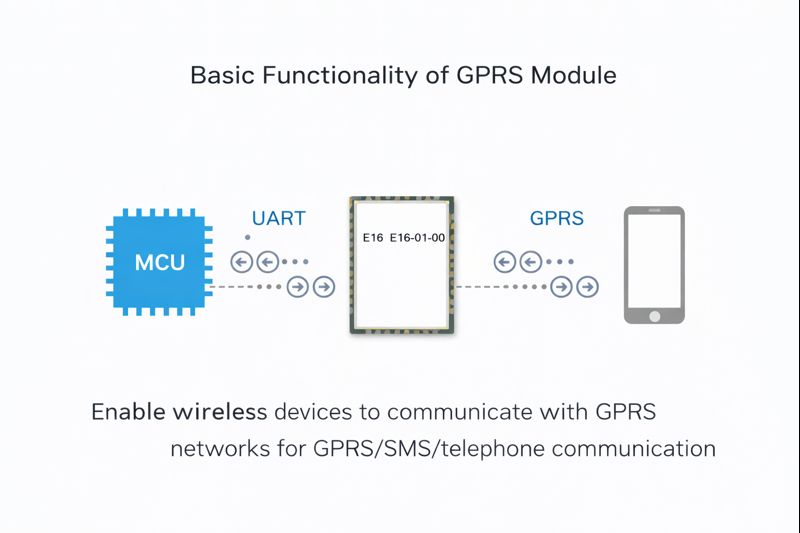
GSM modules connect to external devices via a serial port and support a standard set of AT commands. Users can send AT commands to send/receive SMS, make voice calls, and transmit data. The E16 GPRS AT Command Module is a typical GSM module—it not only inherits the basic functions of GSM modules but also integrates GPRS technology to provide higher data transmission rates and more stable network connections. This allows mobile devices to access the internet more efficiently, meeting the needs of various IoT applications.
So what exactly is a modem? Let’s explore this together.
Understanding Modems
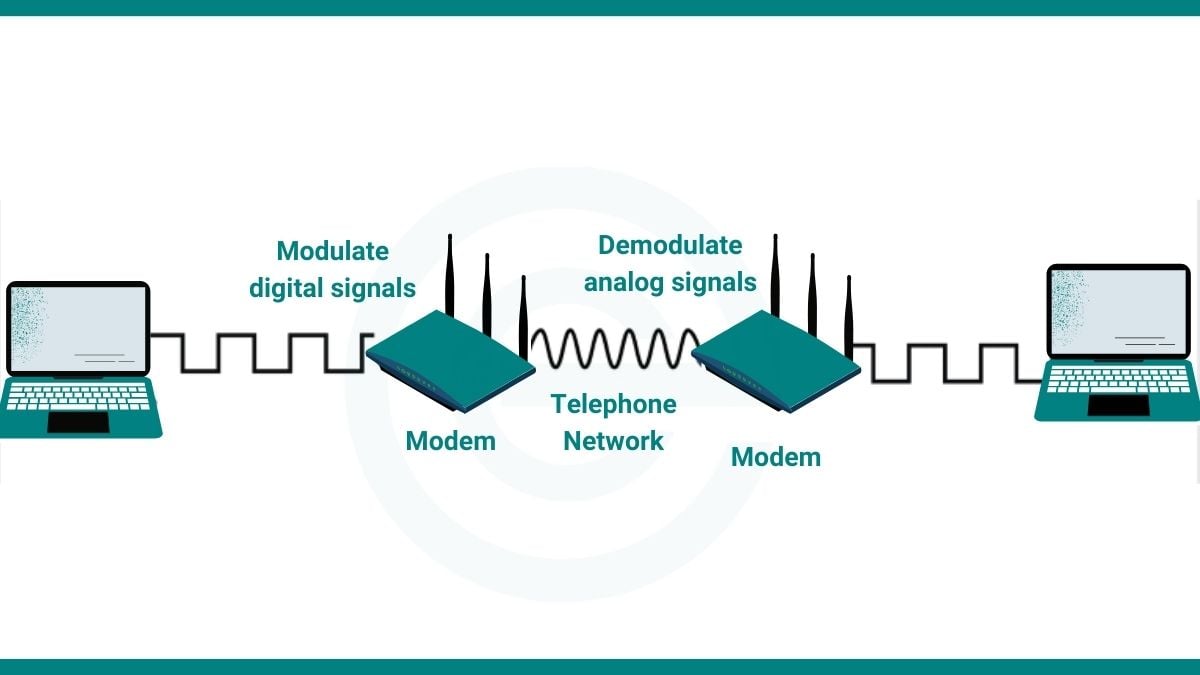
A modem (short for Modulator-Demodulator) is a device that converts between digital and analog signals. In early communications, digital devices like computers generated and processed digital signals, but traditional transmission media such as telephone lines could only carry analog signals. Modems solved this problem by “modulating” digital signals into analog signals suitable for transmission over analog channels. When the signals reach the receiving end, the modem “demodulates” the received analog signals back into digital signals for processing by digital devices.
While transmission media and communication methods have evolved significantly, modems still play a crucial role as a bridge between digital and analog communications. In the E16 GPRS AT Command Module, the modem performs this key function to ensure smooth data transmission.
Functions of Modem
The modem plays an essential role in the E16 GPRS AT Command Module, with its main functions including:
1.Signal Modulation & Conversion: Converts digital signals into analog signals suitable for transmission over wireless channels (modulation process), ensuring data can be effectively transmitted via GPRS networks.
2.Signal Demodulation & Restoration: Demodulates analog signals back into digital signals at the receiving end for processing by microprocessors or other digital devices.
3.Dynamic Rate Adaptation: Supports multiple data transmission rates and automatically adjusts based on network conditions to achieve optimal communication efficiency.
4.Error Detection & Correction: Features data verification and error-correction mechanisms to improve transmission reliability and reduce the risk of data loss or corruption.
Through these functions, the modem ensures the E16 GPRS AT Command Module provides stable and efficient data communication services across various scenarios.
After introducing the modem, we need to delve deeper into the AT commands, as they are the key elements for the E16 GPRS AT command module to function properly.
What is an AT command?
AT commands are a standard set of instructions for controlling modems, named after the “ATtention” command prefix introduced by early modem manufacturer Hayes. This command set enables human-machine interaction through a simple, readable text format. For example:
- Sending AT+CSQqueries signal quality;
- Sending AT+CGDCONTconfigures GPRScontext parameters.
The E16 Module supports AT commands covering core functions such as:
- Network connection management (likeAPN settings);
- SMS sending/receiving (PDU/Text mode switching);
- Call control (call setup/hang-up);
- Data transmission control (transparent/non-transparent mode selection).
By sending these standardized commands via a serial port, developers can quickly build IoT applications without deep knowledge of underlying communication protocols. For instance, a sequence of commands from AT+HTTPINIT to AT+HTTPACTION enables HTTP data upload. This design significantly lowers development barriers, allowing the E16 Module to be widely used in IoT terminals such as smart meters, vehicle trackers, and environmental monitoring devices.

What tasks can AT commands accomplish?
- Retrieve basic information about the mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem: likemanufacturer name (AT+CGMI), model (AT+CGMM), IMEI number (International Mobile Equipment Identity, AT+CGSN), and software version (AT+CGMR).
- Retrieve basic user information: likeMSISDN (AT+CNUM) and IMSI number (International Mobile Subscriber Identity, AT+CIMI).
- Check the current status of the mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem: likedevice activity status (AT+CPAS), mobile network registration status (AT+CREG), wireless signal strength (AT+CSQ), and battery level/charging status (AT+CBC).
- Establish data or voice connections with remote modems: likeATD (dial), ATA(answer).
- Send and receive faxes: likeATD, ATA, AT+F* commands.
- Manage SMS: Send (AT+CMGS, AT+CMSS), read (AT+CMGR, AT+CMGL), write (AT+CMGW), or delete (AT+CMGD) SMS; receive notifications for new SMS (AT+CNMI).
- Manage phonebook entries: Read (AT+CPBR), write (AT+CPBW), or search (AT+CPBF) contacts.
- Perform security tasks: Enable/disable facility locks (AT+CLCK), check if a facility is locked (AT+CLCK), and change passwords (AT+CPWD).Examples of facility locks: SIM lock (requires a password to use the SIM card on startup) and PH-SIM lock (the device is bound to a specific SIM card; a password is needed to use other SIM cards).
- Control the display of AT command result codes/error messages:likeenable/disable specific error messages (AT+CMEE) and set error message format (numeric or detailed, via AT+CMEE=1 or AT+CMEE=2).
- Retrieve or modify configurations of the mobile phone or GSM/GPRS modem: likechange the GSM network (AT+COPS), bearer service type (AT+CBST), radio link protocol parameters (AT+CRLP), SMS center address (AT+CSCA), and SMS storage location (AT+CPMS).
- Save and restore configurations:likesave (AT+CSAS) and restore (AT+CRES) SMS-related settings (such as the SMS center address).
What is the E16 GPRS AT Command Module?
The E16 GPRS AT Command Module is an embedded communication module that integrates GPRS communication technology and a standard set of AT commands. It features a high-performance industrial-grade chip design, wide-temperature operation (-40℃ to +85℃), and supports multi-band GSM/GPRS network access (850/900/1800/1900MHz).
Core Competitive Advantages
1.Built-in TCP/IP protocol stack, enabling direct IoT protocol communication (like HTTP/MQTT).
2.Rich hardware interfaces (UART/SPI/I2C) for easy connection to various microcontrollers.
3.Low-power mode support, with a standby current as low as 1mA—ideal for battery-powered devices.
4.Flexible data transmission configuration via AT commands (transparent transmission/custom protocols), meeting communication needs of scenarios like smart meters, industrial sensors, and vehicle terminals.
5.Built-in watchdog mechanism and heartbeat packet function to ensure stable network connections.
6.Compact size (30mm×40mm), facilitating integration into compact devices.
Module Parameters
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Supply | Voltage: 3.4V–4.2V |
| Power Saving | Current in SLEEP mode: 0.9mA |
| Frequency Bands | GSM850, EGSM900, DCS1800, PCS1900 (auto-search, GSM Phase2/2+ compliant) |
| GSM Type | Mobile Station Class 4 (2W) for EGSM900/GSM850; Class 1 (1W) for DCS1800/PCS1900 |
| GPRS Connectivity | Multi-slot class 12 (default), optional class 10/8 |
| Temperature Range | Operating: -30°C~+80°C; Storage: -45°C~+90°C |
| GPRS Data | Downlink: 68.5kbps; Uplink: 34.3kbps; Supports TCP/IP, PAP, PPP |
| SMS & USSD | Supports USSD, SMS (MT/MO/CB/Tex/PDU modes), SIM card storage |
| SIM & Antenna | SIM: 1.8V/3V; GSM antenna pin |
| Serial & Debug Port | Serial: 2400bps–115200bps, AT commands, GSM 07.10 compliant; Debug: For firmware upgrade |
| Other Features | Real-time clock, timer (AT command configurable), firmware upgrade via debug port |
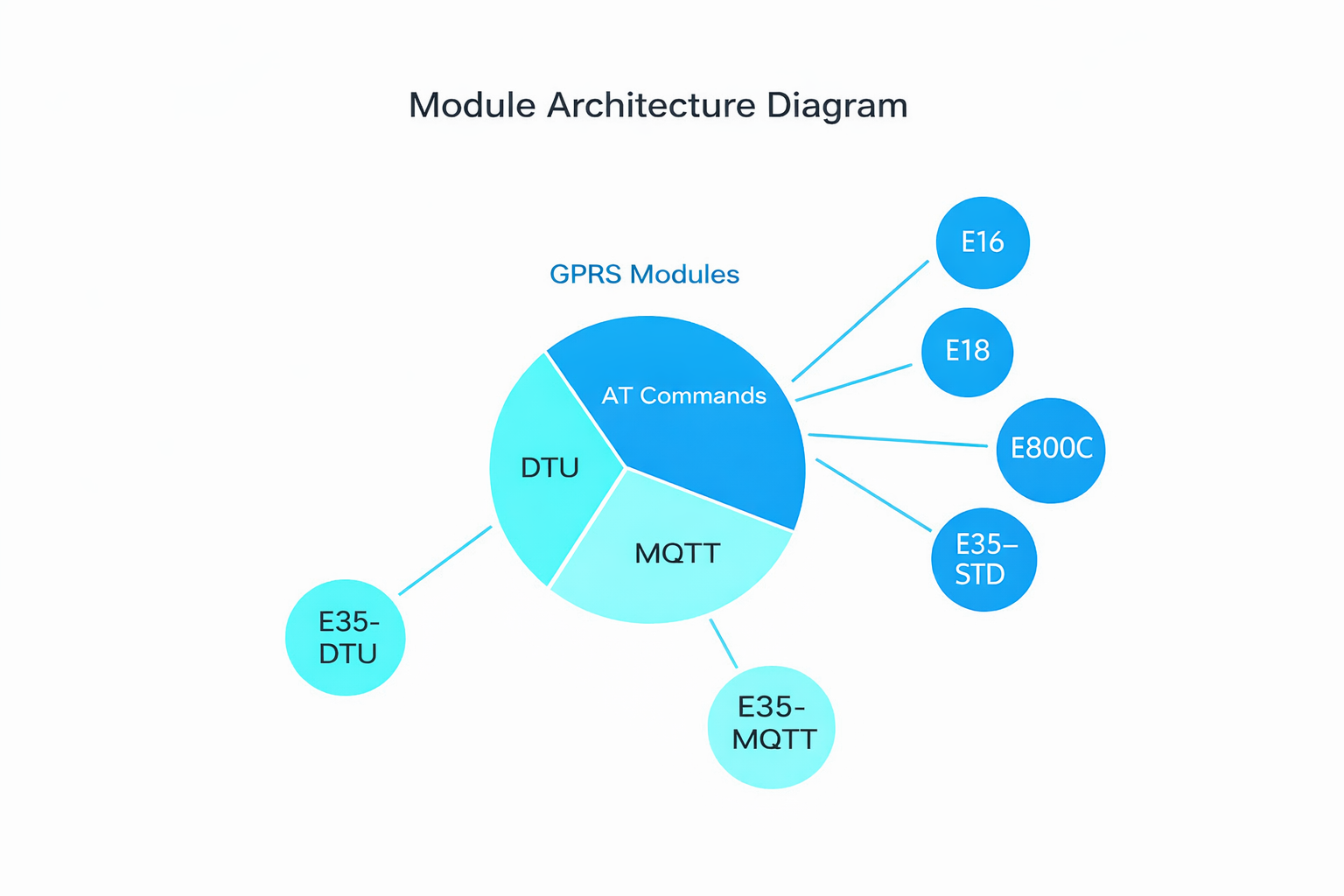
Module Styling Diagram
Basic Functions of GPRS Modules
Serial Port Baud Rate
The serial port baud rate of the E16 GPRS AT command module ranges from 24,000 bps to 460,800 bps.
FAQS
1.What is the AT command for GPRS?
Common AT commands for GPRS include:
- AT+CGDCONT:Defines GPRS context parameters;
- AT+CGACT: Activates or deactivates a PDP context;
- AT+CGATT:Attaches to or detaches from a GPRS network.
These commands allow users to configure and manage GPRS connections—including setting key parameters like APN (Access Point Name), username, and password—ensuring the module connects to the specified GPRS network and transmits data successfully. By using these AT commands flexibly, developers can easily implement GPRS communication with the E16 Module to meet various IoT application needs.
2.Does the GSM module require a SIM card?
Yes, a GSM module must rely on a SIM card to access mobile networks—its working principle is similar to that of a mobile phone. As a user identification module, the SIM card stores critical information such as the IMSI number and authentication key. The module performs two-way authentication with the operator’s network via the SIM card to establish an encrypted communication link.
The E16 Module’s SIM card interface supports dual voltage standards (1.8V/3V), compatible with different types of SIM cards. Users only need to insert a compliant SIM card into the slot, and the module will automatically read the card information and complete network registration.
Notably, some industrial scenarios use soldered SIM cards or eSIM solutions. These designs solder the SIM chip directly to the circuit board, improving device shock resistance and environmental adaptability—ideal for long-running IoT terminals like vehicle trackers and smart meters.
3.How to set APN using AT command?
To set the APN, send the command: AT+CGDCONT=1,”IP”,”your APN name”. Here’s what each part means:
- “1” = PDP context identifier (just use 1 here)
- “IP” = uses the IPv4 protocol
- “your APN name” = replace this with the actual APN provided by your carrier. For example, China Mobile IoT SIMs commonly use “CMIOT”, so the command becomes: AT+CGDCONT=1,”IP”,”CMIOT”.
After sending the command, check the current configuration with AT+CGDCONT?. If the response is +CGDCONT: 1,”IP”,”CMIOT”, the setup worked.
Note: Before doing this:
1.Make sure the SIM card is inserted correctly.
2.Check that the module is registered on the GSM network using AT+CREG? — a response like +CREG: 0,1 or +CREG: 0,5 means it’s registered.
Some carriers require a username and password too. If so, send this extra command: AT+CGAUTH=1,1,”your username”,“your password” to finish the authentication setup.
That’s all for today’s sharing! If you’re interested, feel free to check it out!
